kickstart 2021 roundD
kick start的题目质量非常高,感觉前三题没有问题,自己可以确定前三题做出来。前两题做出来了,后来因为有事,三四题就没有做。第三题不用看解答就能干出来。
Arithmetic Square
题目

地址
https://codingcompetitions.withgoogle.com/kickstart/round/00000000004361e3/000000000082b813
题意
暴力
思路
- 第一题比较简单,大意就是给定一个
3x3的矩阵,求问修改最中间的数,使得上下和对角线的三个数字组成的等差序列最多。暴力尝试所有可能的等差数列即可。
代码
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<set>
#include<unordered_set>
#include<map>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<string>
#include<stack>
#include<algorithm>
#include<limits.h>
using namespace std;
void slove(int t){
int ans = 0;
int curr = 0;
map<int,int> cnt;
vector<vector<long long>> matrix(3,vector<long long>(3));
cin>>matrix[0][0]>>matrix[0][1]>>matrix[0][2];
cin>>matrix[1][0]>>matrix[1][2];
cin>>matrix[2][0]>>matrix[2][1]>>matrix[2][2];
if((matrix[0][1] - matrix[0][0]) == (matrix[0][2] - matrix[0][1])) ans++;
if((matrix[2][1] - matrix[2][0]) == (matrix[2][2] - matrix[2][1])) ans++;
if((matrix[1][0] - matrix[0][0]) == (matrix[2][0] - matrix[1][0])) ans++;
if((matrix[1][2] - matrix[0][2]) == (matrix[2][2] - matrix[1][2])) ans++;
int a = matrix[1][2] - matrix[1][0];
if(a%2 == 0){
cnt[a/2 + matrix[1][0]]++;
}
int b = matrix[2][1] - matrix[0][1];
if(b%2 == 0){
cnt[b/2 + matrix[0][1]]++;
}
int c = matrix[2][2] - matrix[0][0];
if(c%2 == 0){
cnt[c/2 + matrix[0][0]]++;
}
int d = matrix[2][0] - matrix[0][2];
if(d%2 == 0){
cnt[d/2 + matrix[0][2]]++;
}
for(auto v : cnt){
curr = max(curr,v.second);
}
ans += curr;
cout<<"Case #"<<t<<": ";
cout<<ans;
cout<<endl;
}
int main(){
int t;
cin>>t;
for(int i = 0; i < t; ++i){
slove(i+1);
}
return 0;
}
|
Cutting Intervals
题目

地址
https://codingcompetitions.withgoogle.com/kickstart/round/00000000004361e3/000000000082b933
题意
差分数组 + 贪心
思路
- 给定一系列的二维空间中的线段,在限定的切割操作中,求问最多可以把这些线段切成多少段?
- 我们可以参考线段的切割情况如下:
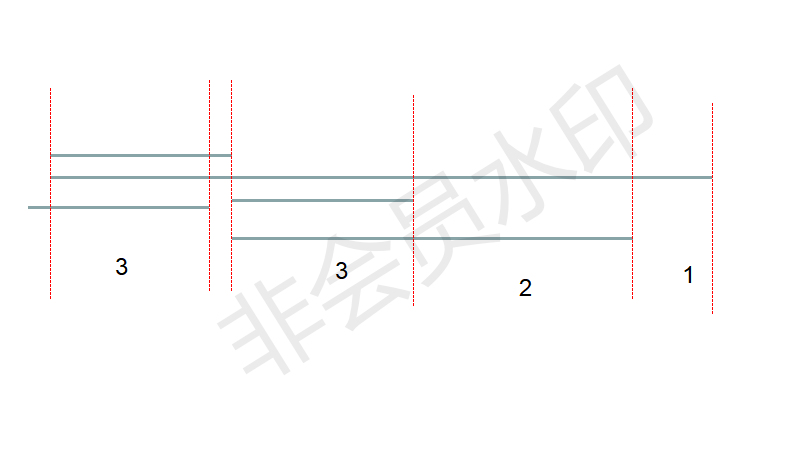
我们可以看到可以利用查分数组,即可计算连续的区间内每切一次可以增加多少条线段,我们设区间$[x,y]$总共有d条线段重合,则我们首先可以知道在区间$[x+1,y-1]$我们每切割一次则可以增加d条线段,但在区间两个端点处需要特殊处理,我们此时需要判断在点$y$处需要特殊处理,因为端点处;我们首先讲可以进行切割的区间加入到待选队列中,并按照重合的次数进行排序。但是我们需要注意的是区间的右端点,需要将右端点为结束端点的线段去掉。|__|__|________| | | |
| | |________|__|________| |
| |——|————————|——| | |
| | | |__|________|_____|
1 2 3 6 7 10 12
|
- 如上图所示,我们可以看到在区间
[1,2]之间只有1条线段重合,在区间[2,3]之间有两条线段重合,在区间[3,6]之间只有3条线段重合,[6,7]之间有3条线段重合,[7,10]之间有两条线段重合,[10,12]之间有两条线段重合。我们知道区间分布如下:
[1,2]无法分割。[2,3]无法分割。[3,6]在(4,5)处每分割一次即可增加3个线段但在6处进行分割只能增加两条线段。[7,10]在(8,9)处分割每分割一次即可增加2个线段,但在10分割只能增加1个线段[10,12]在(11)处分割每分割一次即可增加1个线段,但在12处无法分割。
- 我们利用查分数组很快即可以计算出每个区间内重叠的线段的次数,并按照次数的大小进行排序即可,我们使用贪心策略,每次选取分割区间最大的点即可。
代码
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<set>
#include<unordered_set>
#include<map>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<string>
#include<stack>
#include<algorithm>
#include<limits.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
void slove(int t){
long long ans = 0;
long long n,c;
map<long long,int> prev;
map<long long,int> arrl;
map<long long,int> arrr;
cin>>n>>c;
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i){
long long l,r;
cin>>l>>r;
prev[l]++;
prev[r]--;
arrl[l]++;
arrr[r]++;
}
ans = n;
map<long long,long long> arr;
long long left = -1;
long long curr = 0;
for(auto v : prev){
if(curr == 0){
left = v.first;
curr += v.second;
}else{
arr[curr] += v.first - left - 1;
arr[curr-arrr[v.first]]++;
left = v.first;
curr += v.second;
}
}
for(auto it = arr.rbegin(); it != arr.rend(); it++){
long long x = min(c,it->second);
ans += x*it->first;
c -= x;
if(c <= 0) break;
}
cout<<"Case #"<<t<<": ";
cout<<ans;
cout<<endl;
}
int main(){
int t;
cin>>t;
for(int i = 0; i < t; ++i){
slove(i+1);
}
return 0;
}
|
Final Exam

地址
https://codingcompetitions.withgoogle.com/kickstart/round/00000000004361e3/000000000082bffc
题意
二分查找
思路
- 感觉第三题要比第二题简单许多,就是一个典型的二分查找的应用即可。我们知道给定难度
P,则我们知道绝对值最小值得点肯定在距离点p最近的两个区间,我们利用二分查找,查找距离点p最近的两个区间$[l_{1},r_{1}],[l_{2},r_{2}]$且满足$l_{1}\le r_{1}\le l_{2}\le r_{2}$,如果点p在区间$[l_{1},r_{1}]$范围内,则我们可以知道当前最小的绝对值为0,则我们将p从区间内取出,并将原有区间$[l_{1},r_{1}]$划分为两个新的区间$[l_{1},p-1],[p+1,r_{1}]$,并将这两个新的区间加入到待选序列中。________ | __________
[l1,r1] p [l2,r2]
|
- 如果不在区间内,则肯定距离
p最近的点要么为$r_{1},l_{2}$,则我们优先从这两个点中选择距离最近的点即可,假设$r_{1}$距离点p最近,则我们将$r_{1}$从区间内取出,然后再更新区间为$[l_{1},r_{1}-1]$.
代码
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<set>
#include<unordered_set>
#include<map>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<string>
#include<stack>
#include<algorithm>
#include<limits.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
void slove(int t){
int n,m;
map<LL,LL> pb;
vector<LL> ans;
cin>>n>>m;
vector<LL> arr = vector<LL>(m);
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i){
LL a,b;
cin>>a>>b;
pb[b] = a;
}
for(int i = 0; i < m; ++i){
cin>>arr[i];
auto it = pb.lower_bound(arr[i]);
if(it == pb.end()){
it--;
ans.push_back(it->first);
LL a = it->first;
LL b = it->second;
pb.erase(a);
a--;
if(a >= b) pb[a] = b;
}else{
LL a = it->first;
LL b = it->second;
if(it->second > arr[i]){
if(it == pb.begin()){
ans.push_back(b);
b++;
pb.erase(a);
if(b <= a) pb[a] = b;
}else{
it--;
LL c = it->first;
LL d = it->second;
if(abs(arr[i]-c) > abs(arr[i] - b)){
ans.push_back(b);
b++;
pb.erase(a);
if(b <= a) pb[a] = b;
}else{
ans.push_back(c);
pb.erase(c);
c--;
if(d <= c) pb[c] = d;
}
}
}else{
ans.push_back(arr[i]);
LL c = arr[i] - 1;
LL d = arr[i] + 1;
pb.erase(a);
if(c >= b) pb[c] = b;
if(d <= a) pb[a] = d;
}
}
}
cout<<"Case #"<<t<<": ";
for(int i = 0; i < ans.size(); ++i){
cout<<ans[i]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
int main(){
int t;
cin>>t;
for(int i = 0; i < t; ++i){
slove(i+1);
}
return 0;
}
|
欢迎关注和打赏,感谢支持!






