中国银联专场竞赛(2023届校园招聘专场)
这个专场赛的题目不咋的,全都是业务逻辑的题目,少了些思考性的题目。
银联-1. 重构链表
题目
给定一个链表的头节点 head ,在不改变节点顺序的基础下,请删除链表中所有值为 偶数 的节点,并返回这个链表 。
注意:
- 若链表为空,则返回空值。
示例 1:
输入:
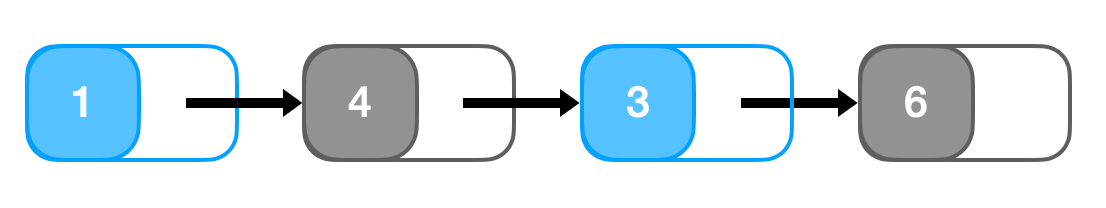
head = [1,4,3,6]输出:
[1,3]解释:如下图所示,黑色节点的值均为偶数,删除这些节点后,链表为
[1,3]
示例 2:
输入:
head = [5,7,9,9,1]输出:
[5,7,9,9,1]解释:原链表中不存在值为偶数的节点。
示例 3:
输入:
head = [2,4]输出:
[]解释:原链表中所有节点值均为偶数。
提示:1 <= head.length <= 10^50 <= Node.val <= 100
地址
https://leetcode.cn/contest/cnunionpay2022/problems/VLNEbD/
题意
链表
思路
- 直接统计偶数元素,然后重建链表即可。
- 复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:$O(n)$,其中 $n$ 表示链表的长度。
- 空间复杂度:$O(n)$,其中 $n$ 表示链表的长度。
代码
/** |
银联-2. 勘探补给
题目
工程部在一条坐标轴上设立了若干补给站,station[i] 表示编号为 i 的补给站的坐标。
现在有一些正在执行任务的勘探队需要进行补给,pos[i] 表示第 i 个勘探队当前所在位置的坐标。勘探队将优先选择当前距离最近的补给站进行补给。若两座补给站距离相同,则选择坐标更小的那一个。
请按顺序返回这些勘探队所选择的补给站编号。
注意:
station中的元素严格递增,即station[i] < station[i+1]
示例 1:
输入:
station = [2,7,8,10]pos = [4,9]
输出:[0,2]
解释:
坐标4的勘探队与坐标为2和7的补给站距离分别为2和3, 选择坐标为2的补给站
坐标9的勘探队与坐标为8和10的补给站的距离均为1, 选择坐标更小为8的补给站
返回编号为[0,2]的补给站。
示例 2:
输入:
station = [2,5,8,14,17]pos = [1,14,11,2]
输出:[0,3,2,0]
提示:
1 <= pos.length,station.length <= 10^41 <= pos[i] <= 10^61 <= station[i] < station[i+1] <= 10^6
地址
https://leetcode.cn/contest/cnunionpay2022/problems/6olJmJ/
题意
双指针或者二分查找
思路
- 几乎是模板题目了,感觉直接二分查找即可,找到距离每个
pos最近的station即可,非常简单的二分查找。 - 复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:时间复杂度为 $O(m \log n)$,$m,n$ 表示
pos, station的长度。 - 空间复杂度:空间复杂度为 $O(1)$,除返回值外不需要额外的空间。
代码
class Solution { |
银联-3. 风能发电
题目
现有一座风力发电场和容量 storeLimit 的储能站,第 j 条供电指令 supply[j]=[time, minSupply, maxSupply] 表示时刻 time 起(包含该时刻)每一时刻最少供应电能 minSupply 以及最多供应电能 maxSupply,直至后续指令调整。
在时刻 i 发电量为 power[i],该时刻供电逻辑如下:
若发电量在
[minSupply, maxSupply]范围内,则均供应负载;若发电量大于
maxSupply,则超出部分存入储能站,存储量至多不超过storeLimit;若发电量小于
minSupply
,则由储能站补充缺少电量,最多不超过当前存储量;
注:储能站补充电量,直至剩余存储电量为
0
请返回最后时刻(即时刻 power.length-1)储能站中能源总量。
注意:
- 输入用例保证供电指令的
time严格递增且第0个指令的time = 0 - 储能电站初始存储电量为
0
示例 1:
输入:
storeLimit = 10power = [1,3,4,3,6]supply = [[0,2,3]]输出:
4解释:
时刻 0,供能 1, 新增储能 0, 总储能 0
时刻 1,供能 3, 新增储能 0, 总储能 0
时刻 2,供能 3, 新增储能 1, 总储能 1
时刻 3,供能 3, 新增储能 0, 总储能 1
时刻 4,供能 3, 新增储能 3, 总储能 4
因此最后时刻,剩余的能源总量为 4
示例 2:
输入:
storeLimit = 6power = [6,5,2,1,0]supply = [[0,1,2],[2,3,3]]输出:
0解释:
时刻 0,供能 2, 新增储能 4, 总储能 4
时刻 1,供能 2, 新增储能 2, 总储能 6 (由于储能电站达上限,电量 1 丢弃)
时刻 2,供能 3, 新增储能 -1, 总储能 5
时刻 3,供能 3, 新增储能 -2, 总储能 3
时刻 4,供能 3, 新增储能 -3, 总储能 0
因此最后时刻,剩余的能源总量为 0
提示:
1 <= storeLimit <= 10^61 <= power.length <= 10^50 <= power[i] <= 10^51 <= supply.length <= power.length- 对于
i < j,满足supply[i][0] < supply[j][0] supply[i].length == 30 <= supply[i][0] < power.length0 <= supply[i][1]<= supply[i][2] <= 10^5
地址
https://leetcode.cn/contest/cnunionpay2022/problems/wMGN0t/
题意
直接模拟
思路
- 由于
supply从0开始,因此我们直接模拟从最小的开始即可:- 如果
power小于supply则减少储能即可; - 如果
power大于supply则增加储能即可; - 最终返回最后的储能结果即可;
- 如果
- 复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:时间复杂度为 $O(n + m)$,$m, n$ 为
power, supply的长度。 - 空间复杂度:空间复杂度为 $O(m)$,$m$ 为数组的长度。
代码
class Solution { |
银联-4. 设计自动售货机
题目
「银联二维码」支付可以提供简便、顺畅的消费服务,通过出示二维码或扫描二维码即可完成支付。
现有一台使用银联二维码进行支付的自动售货机,并对使用 银联 支付的用户提供额外的优惠服务。
同一名顾客每成功购买一次,下次购买便可多享受 1% 的折扣(折后价向上取整),最低折扣为 70%
- 即:第一次购买支付 100% 费用,第二次购买支付 99% 费用, 第三次购买支付 98% 费用,以此类推。
请你设计一个自动售货机,你需要实现一个 VendingMachine 类:
VendingMachine()—— 初始化一个VendingMachine实例void addItem(int time, int number, string item, int price, int duration)time
—— 在
number
时刻向售货机中增加
item
个名称为
price
的商品,价格为
duration
,保质期为
—— 在
- 同种商品可能有不同批次,不同批次的价格和保质期可能不同
- ```
long sell(int time, string customer, string item, int number)时刻,名称为time
的顾客前来购买了customer
个名称为number
的商品,返回总费用 - 当且仅当售货机中存在足够数量的未过期商品方可成功购买,并返回支付的总费用,否则一件商品也不会售出,并返回 `-1` - 对于价格不同的同种商品,优先售出价格**最低**的商品; - 如果有价格相同的同种商品,优先出售**距离过期时间最近**的商品;item
注意:
- 输入保证前一次操作的
time不大于后一次操作的time - 过期指商品存入的时刻与保质期之和小于当前时刻,也即
addtime + duration < currTime
示例 1:
输入:
["VendingMachine","addItem","sell","sell","sell","sell"][[],[0,3,"Apple",10,10],[1,"Tom","Apple",1],[2,"Tom","Apple",3],[3,"Mary","Banana",2],[11,"Jim","Apple",1]]输出:
[null,null,10,-1,-1,-1]解释:
VendingMachine sys = new VendingMachine();sys.addItem(0,3,"Apple",10,10);// 时刻0,添加3个Apple,价格为10,保质期为10。sys.sell(1,"Tom","Apple",1);// 时刻1,用户Tom购买1个Apple, 支付10:。sys.sell(2,"Tom","Apple",3);// 时刻2,售货机中Apple数量为2,用户Tom购买失败,返回-1。sys.sell(3,"Mary","Banana",2);// 时刻3,售货机中没有Banana,用户Mary购买失败,返回-1。sys.sell(11,"Jim","Apple",1);// 时刻11,售货机中的Apple全部过期,用户Jim购买失败,返回-1。
示例 2:
输入:
["VendingMachine","addItem","addItem","sell","addItem","sell","sell","sell","addItem","sell","sell"][[],[0,1,"Apple",4,3],[1,3,"Apple",4,2],[2,"Mary","Apple",2],[2,1,"Banana",2,5],[4,"Jim","Banana",2],[4,"Mary","Banana",1],[4,"Mary","Apple",1],[6,200,"Apple",2,5],[6,"Jim","Apple",100],[7,"Mary","Apple",100]]输出:
[null,null,null,8,null,-1,2,-1,null,200,196]解释:
VendingMachine sys = new VendingMachine();sys.addItem(0,1,"Apple",4,3);// 时刻0,添加1个Apple,价格为4,保质期为3。sys.addItem(1,3,"Apple",4,2);// 时刻1,添加3个Apple,价格为4,保质期为2。sys.sell(2,"Mary","Apple",2);// 时刻2,用户Mary购买2个Apple,支付8。sys.addItem(2,1,"Banana",2,5);// 时刻2,添加1个Banana,价格为2,保质期为5。sys.sell(4,"Jim","Banana",2);// 时刻4,售货机中Banana数量为1,用户Jim购买失败,返回-1。sys.sell(4,"Mary","Banana",1);// 时刻4,用户Mary购买1个Banana,享受 1% 的优惠,向上取整后为2sys.sell(4,"Mary","Apple",1);// 时刻4,售货机中的Apple全部过期,用户Mary购买失败,返回-1。sys.addItem(6,200,"Apple",2,5);// 时刻6,添加200个Apple,价格为2,保质期为5。sys.sell(6,"Jim","Apple",100);// 时刻6,用户Jim购买100个Apple。返回 200sys.sell(7,"Mary","Apple",100);// 时刻7,用户Mary购买100个Apple,可享受 2% 的优惠。返回196
提示:
1 <= item.length,customer.length <= 10,item和customer中只包含英文字母1 <= duration,price,number <= 10^60 <= time <= 10^6addItem和sell的总调用次数不超过1000次
地址
https://leetcode.cn/contest/cnunionpay2022/problems/NyZD2B/
题意
堆 + 直接模拟
思路
- 题目本身不是很难,我们需要统计每个顾客的购买次数,并同时存储每个批次的商品。
- 每次添加产品时,将产品的价格、过期时间、数量作为一个批次添加到商品的信息中,并按照价格、过期时间、数量进行排序即可;
- 每次购买商品时,首先将当前商品中的过期的批次全部剔除掉,然后统计剩余的产品数量是否满足顾客的购买要求,如果不能满足购买要求则直接返回;
- 如果满足购买要求,依次按照题目要求的顺序从存储的货物中挑选适合数量的产品,并将每个批次的数量按照题目依次进行剔除掉。
- 在此我们为了方便计算使用
treeset保存相关数据。
- 复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:$O(n^2)$,其中 $n$ 表示
addItem的执行次数。 - 空间复杂度:$O(n)$,其中 $n$ 表示
addItem的执行次数。
代码
class VendingMachine { |
欢迎关注和打赏,感谢支持!
- 关注我的博客: http://mikemeng.org/
- 关注我的知乎:https://www.zhihu.com/people/da-hua-niu
- 关注我的微信公众号: 公务程序猿

扫描二维码,分享此文章